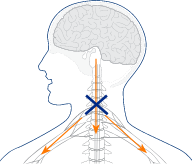
Spasticity occurs when there’s a communication problem between the muscles and the
brain or spinal cord
- In people with multiple sclerosis (MS), the covering of the nerves in the brain and spinal cord that control movement are damaged

Spasticity causes a tightness or stiffness in the muscles and can prevent normal
movement
- Typically occurs in the legs, groin, and buttocks
- Some people experience spasticity in their back
- It can also affect the arms, hands, and even speech

Managing spasticity
Exercise: Helps maintain range of motion and prevent muscles from
contracting. You can work with physical and/or occupational therapists

Medicines:
- Muscle relaxants (eg, baclofen)
- Benzodiazepines
- Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists
- Botulinum toxins

Orthotic devices: Braces and splints can prevent spasms and reduce
muscle tightening

Relaxation techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation, yoga,
meditation, and deep breathing
Massage: Relaxes muscles, expands range of motion, and prevents
pressure sores
The symptoms of spasticity

Muscle stiffness

Muscle spasms

Involuntary contractions

Muscle fatigue

Muscle and joint deformities
Difficulty walking, sitting, and/or sleeping